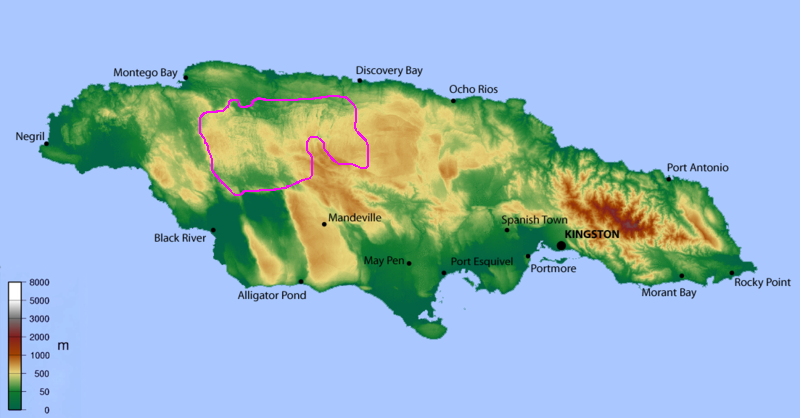
Cockpit Country
Diagram showing the outline of the Cockpit Country
In this article:
What is Karst Cockpit
Karst Cockpit in Jamaica
Biodiversity of the Cockpit Country
Threats to the Cockpit Country
Cultural Significance of the Cockpit Country
1.What is Cockpit karst
Cockpit Karst is a form of polygonal karst where the karst limestone has formed a repetitive pattern of hills and valleys. The peak of these hills are round in shape leading down into the valleys. This formation resembles the bottom of an egg carton.
2. Cockpit Karst in Jamaica
This unique landscape can be found in the moist limestone forest of the Cockpit Country in Central Jamaica.
The Cockpit Country spans the parishes of St. James, Trelawny, Manchester and St. Elizabeth with the majority of the forests being in Trelawny.
The main conservation area contains approximately 22,327 hectares of forest reserves and is 450 km2 in size.
3. Biodiversity of the Cockpit Country
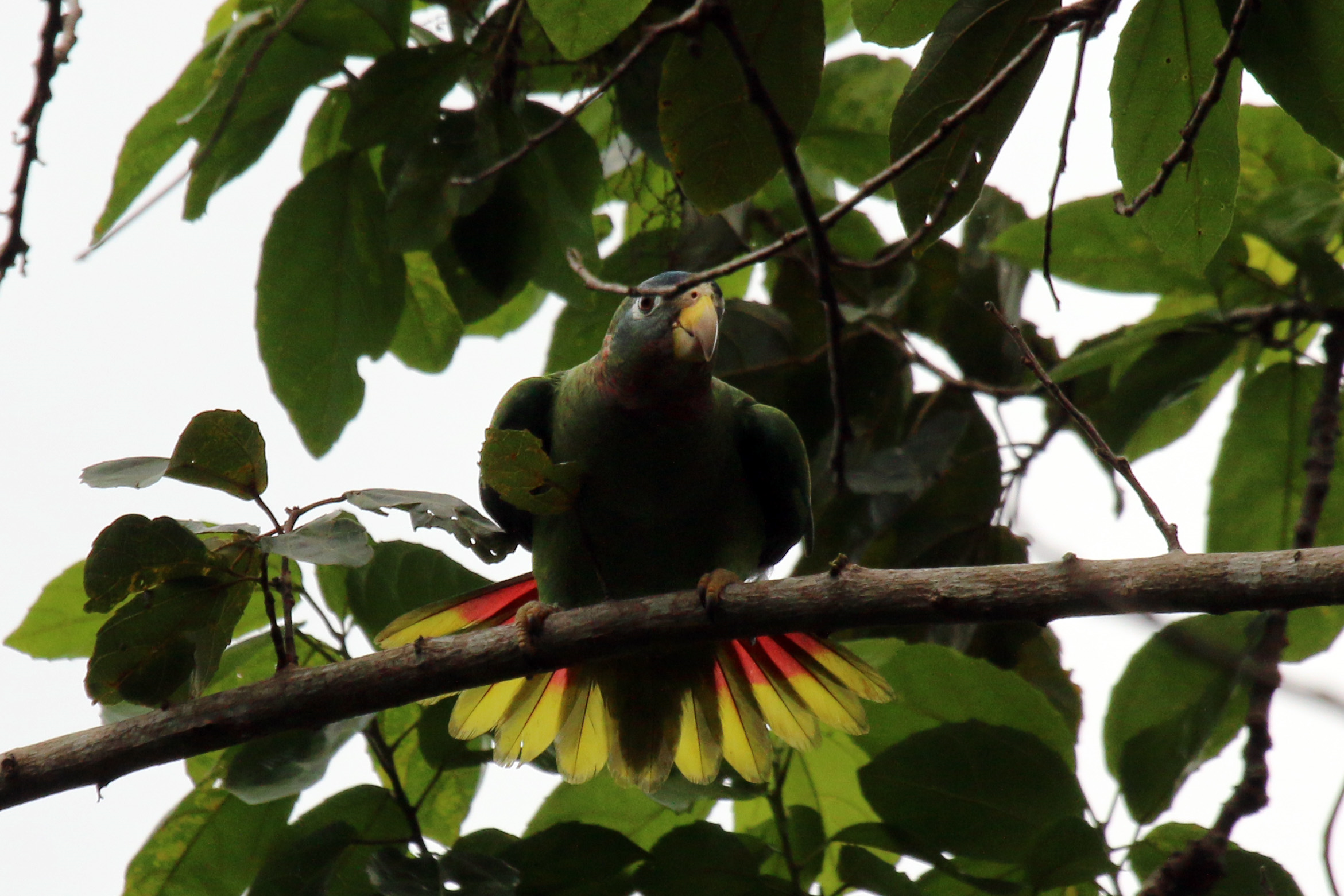
The Cockpit Country is biodiversity hotspot within a hotspot with a high rate of plant and animal endemism. Several of these species are dependent on the Cockpit Country for survival . Endemic species such as the Jamaican Boa,Homerus Swallowtail, Black-Billed and Yellow-Billed Parrots and a variety of frogs can be found in these forests.
The Cockpit Country has one of the highest rates of plant endemism in the entire Caribbean and 60% of Jamaica’s endemic vascular plants can all be found there including a fern endemic to the Cockpit Country.
The Cockpit Karst topography has resulted in certain endemic species being confined to certain areas. It has been observed that neighbouring hilltops often will not have all the same plant species and even display endemism.
Caves in the Cockpit Country such as the Windsor Great Cave and Marta Tick Cave are havens for bat species in Jamaica including the endemic Jamaican Flower Bat and the Jamaican Fig-Eating Bat.
4. Threats to the Cockpit Country
The major factors affecting the plants and animals of the Cockpit Country are bauxite mining and habitat degradation due to agriculture and development. Along with clearing the land for farming, farmers are also guilty of cutting down trees to use as yam sticks.
Several endemic species are forest dependent and can only be found in the Cockpit Country. The Cockpit Country is a primary water resource for Western Jamaican and is also the source for major rivers such as the Martha Brae, Black River, Rio Bueno, Montego River and Great River.
5. Cultural significance of the Cockpit Country
The Cockpit Country is the scene of the Second Maroon War which took place in 1795 and 1796. The Second Maroon War was between the Trelawny Town Maroons and the British.
The treaties signed by the Leeward & Winward Maroons and the British in 1739 were thought to be violated by the British after the flogging of two Trelawny Town Maroons who were accused of stealing pigs by a runaway slave they had returned to their owner (a condition of their signed treaty).
The Maroons retaliated by raiding plantations, killing their owners and releasing slaves.
In the end the Maroons were outnumbered and surrendered to the British who deceived the Maroons and resulted in around 500 Trelawny Town Maroons being deported to Nova Scotia and then Sierra Leone.